Higher Level Geometry and Trigonometry
Higher Level Geometry and Trigonometry
Radians
- Although degrees are the units you are familiar with, the IB uses radians to communicate angles
- They relate the size of an angle to the distance to a point round the circumference of a circle
- 360° = 2π radians
Length of an arc
- Formula (given in formula booklet): length = radius x θ (in radians)
Area of a sector
- Formula (given in formula booklet): Area= 0.5 x θ (in radians) x radius x radius
- So basically: 0.5 x angle x radius squared
Sine rule implication
- When using the sine rule to find angles, there are two possible answers
- To find both, use your first answer, and do (180 – Answer) to find the other possible answer
Tangent function
- It is defined as the ratio of the sine function to the cosine function
- tan θ = sin θ ÷ cos θ
- This formula is included in the formula booklet
Pythagorean identity
- Straight forward formula to find cos or sin of θ
- Simply use roots and rearranging to find the value of the desired function
- This formula is given in the formula booklet:
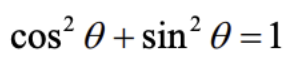
Matrice transformations
- These functions are given in the formula booklet
- They are used to transform matrices
- To check if they are correct, use your GDC to plot the position of each point
- Formulas:

Exam Tip
Make sure that you are able to distinguish between a stretch and an enlargement, as although the matrices are similar, they have different functions
Combining matrix transformations
- If the transformation with matrix A is followed by the transformation with matrix B, the combined transformation has matrix BA

