Finance
2.6 Profitability and Liquidity Ratio Analysis
Profitability Ratios
Gross Profit Margin
- Measures an organization's gross profit as a percentage of sales revenue.
- Remember: Gross profit = revenue (profit) after deducting the direct costs.
- Firms aim to have a high gross profit margin as it indicates good profitability.
- To improve ratio: increase sales revenue or decrease direct costs.
- Formula:

(Net) Profit Margin
- Measures the overall profit after all costs have been deducted as a percentage of sales revenue; businesses aim to have a high percentage as it indicates good control of costs.
- Indicator of how well a business manages its indirect costs.
- To improve ratio: find ways of reducing costs (both direct and indirect) or increase sales revenue.
- Formula:

Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
- Measures a firm's efficiency of using capital invested into the business to generate profit; firms aim to have a high percentage as it indicates capital efficiency.
- Remember: capital employed = non-current liabilities + equity.
- It measures the percentage of profit before interest and tax that the capital employed generates.
- To improve ratio: increase level of profit without introducing capital into business, maintain level of profit whilst reducing amount of capital in business, and decreasing costs and expenses.
- Formula:

Liquidity Ratios
Ratios that measure an organization's ability to pay its short-term debts and liabilities.
- Liquidity = ease of selling an asset and converting it into cash.
- Working capital = current assets – current liabilities.
Current Ratio
- Measures a business' ability to meet its short-term debts.
- A too high ratio indicates inefficiency as a business is keeping too much current assets.
- A ratio below 1 means a business is not able to pay off their short-term obligations with their current assets.
- To improve ratio: increase current assets (e.g. improve cash flow) or decrease liabilities (e.g. negotiate interest terms with suppliers).
- Formula:
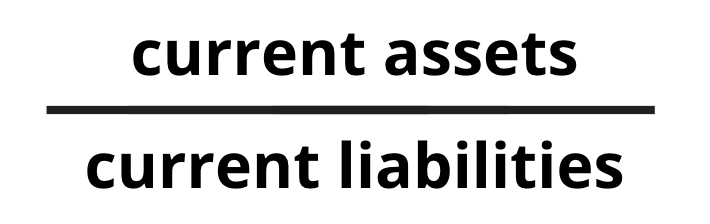
Acid Test Ratio
- Used to measure the ability of an organization to pay off its short-term liabilities without the need to sell any stock.
- Stocks are ignored in this ratio as they are not highly liquid.
- To improve ratio: increase current assets (e.g. improve cash flow) or decrease liabilities (e.g. negotiate interest terms with suppliers).
- Formula:

Exam Tip
There is no need to memorize these formulas, as they are given in the formula booklet

