Marketing
3.2 Marketing planning
Market segment
- Group of people within the wider market that have specific common characteristics that make them behave similarly when in their buying behavior
Market planning
- Marketing is the process of identifying customer needs producing a solution to those needs and delivering the solution to the people who have those needs
- Is the process of formulating marketing strategies and tactics so a business can achieve its objectives
Market segmentation
- The practice of dividing your target market into approachable groups with similar needs or characteristics
- There are 3 main types of segmentation:
- Demographic
- Geographic
- Psychographic
Advantages
- Identify gaps and opportunities in the market
- Design specific products that are tailored to specific markets
Disadvantages
- Not everyone in a segment will behave the same
- Can be hard to identify a segment as consumers can behave to multiple segments at once
- Requires market research which is costly
Targeting
- Refers to the process of selecting a target market
TOOL: BCG Matrix
- This tool helps businesses that have multiple products to decide their marketing strategies
- Here is the tool:

- Cash cows: not much investment needed as they are mature products that bring high sales volume
- Dogs: usually products at the end of their life cycle or after a failed launch
- Stars: require a lot of investment to keep up with high market growth
- Question mark: Products that launched but didn't gain much market share. It requires a lot of investment but can provide a lot of success if the market likes it.
Limitation
- Doesn't consider synergies between products
- Does not consider external environment that can impact the success of a product
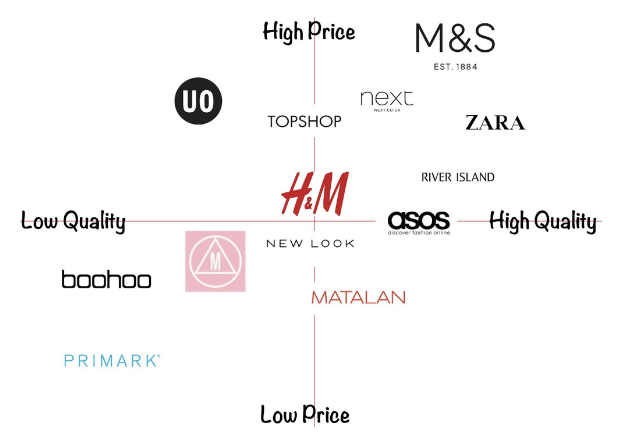
TOOL: Product positioning maps
- Are visual representations of how consumers see the companies based on 2 axes
- It is useful to:
- Identify market segments whose needs are not fulfilled
- Occupy gaps in the market
- Help businesses identify competition
Example:
Markets
- There are two types of markets:
- Niche markets
- Mass markets
Niche markets
- Are specialized products aimed at a subset of a larger market
- Usually happens with small scale production; no economies of scale
- Prices tend to be high due to limited competition and high customer loyalty
Mass markets
- Products aimed at broad market segments
- Likely large-scale production
Unique selling point
- Is a factor which differentiates a product service or brand from its competitors
- Helps a brand stand out
- Helps lead to customer loyalty
Disadvantages
- Likely requires investment in research and development
- Might not attract a large portion of the market
- Competitors may copy it
Differentiation
- It is an attempt of a business to distinguish its products from those of its competitors adding value to it.
- Helps increase demand for products increasing brand loyalty
- Examples:
- Price
- Product
- Place
- Promotion
Porter's Generic Strategies
- Used to identify generic strategies a business can adopt to stay competitive in the market
- Pursuing multiple strategies is not sustainable in the long term
Limitation:
- A business that is stuck in the middle isn't differentiated enough to convince customers to buy products.
Tool:
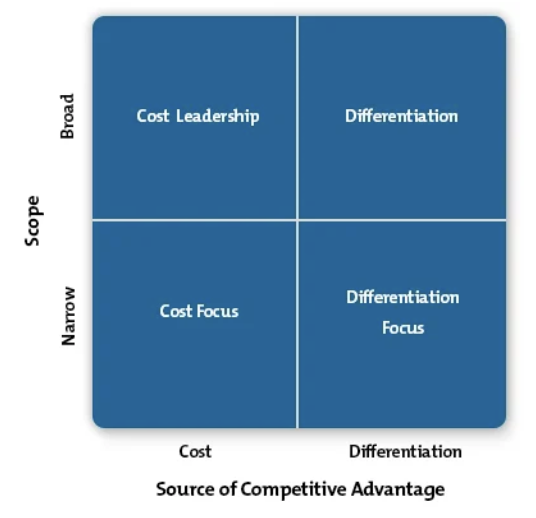
- The scope is the market: either mass or niche
- Cost leadership: becomes low-cost producer in the industry
- Differentiation: when a business makes its products different from its competitors
- Cost focus: becomes low-cost producer in niche market
- Differentiation focus: business produces specialized or differentiated products in a niche market
Exam tip
Be careful not to be confused with "cost". It is the cost of production and not the price of the product.

