Introduction to Business Management
1.3 Business Objectives
Vision statement:
A vague statement of what the organization would like to achieve and be in the long term (distant future).
Mission statement:
Specifies the business' purpose of existence, who they are, and what they do. It provides a sense of direction to the business in terms of what to accomplish or pursue.

Business aims:
Long-term aspirations of an organization (overall target/goal).
Business objectives:
- SMART targets that must be achieved to reach those aspirations (smaller targets that help reach that goal).
- Aims and objectives align all the efforts of all employees towards a common vision and ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal, helping give them purpose.
Targets businesses set must be SMART:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic/relevant
- Time-bound
Common objectives:
- Profit
- Growth: increase in a certain metric(s) (e.g. market share, sales revenue, etc.)
- Shareholder value: usually refers to dividends or share price increase
- Ethical matters: tasks/targets that go beyond profit-making and are in line with moral behavior, sustainability, and CSR. Usually adopted by social enterprises.
Strategy vs Tactic:
Strategy: is how generally. It is the path from going where we are today to where we want to go (goal). General plan to reach the objective.
Tactic: Specific things, often tangible, that a business must do to achieve their strategy.
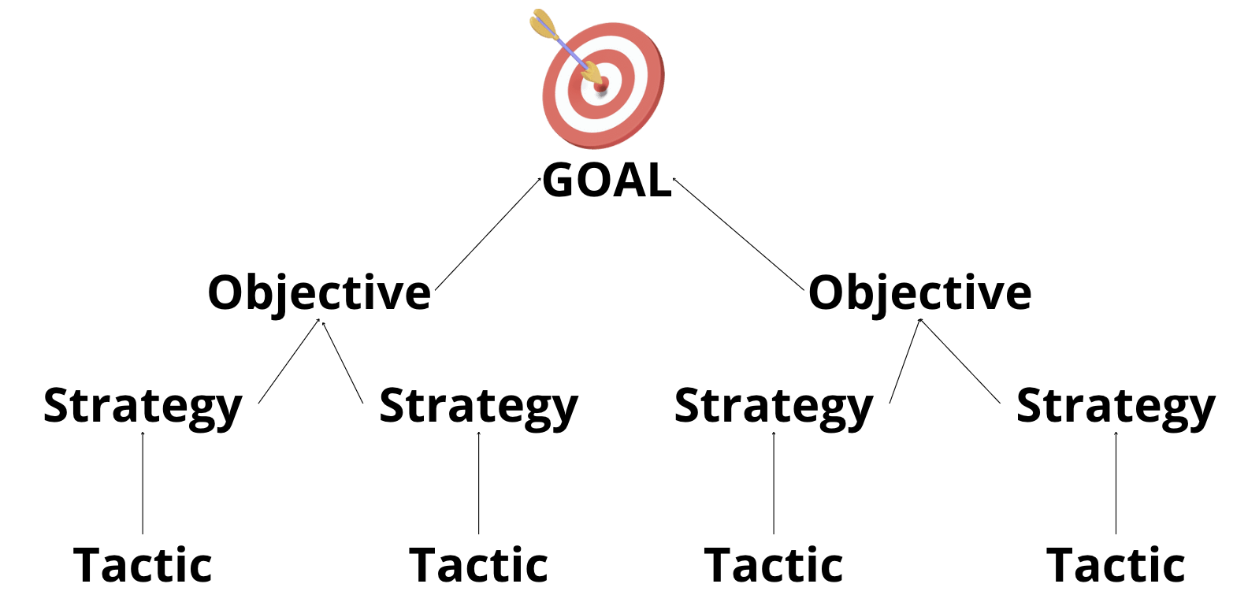
Example:
For a video game business their goal, objective, strategy, and tactic may be the following:
- Goal: Earn 40% market share of the video game global market
- Objective: By the end of the year reach 20% market share in each of the main markets: USA, China, Japan, and Russia.
- Strategy: Provide the best video games via our platform for all target markets based on gender, age, and income.
- Tactic: Upload new games frequently to our platform based on reviews collected by the marketing team.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Concept that businesses have a responsibility to consider and positively impact society beyond their economic interests.
- Business morally accepts their obligation to society and not only shareholders.
- Idea where companies voluntarily integrate social and environmental concerns into their business operations and interactions with stakeholders.
Benefits of CSR:
- Reduced energy expenses
- Reduced waste expenses
- Reduced material expenses
- Increased productivity
- Reduced turnover
- Increased media exposure and reputation
- Brand loyalty
- Reduced risk
- Better reputation may lead to increased investments

